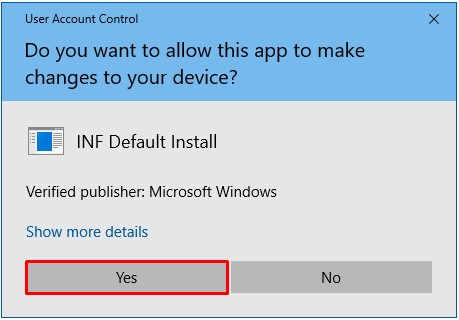
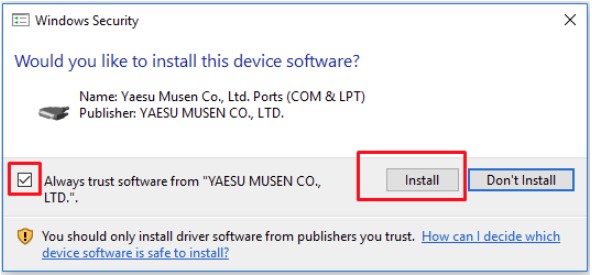
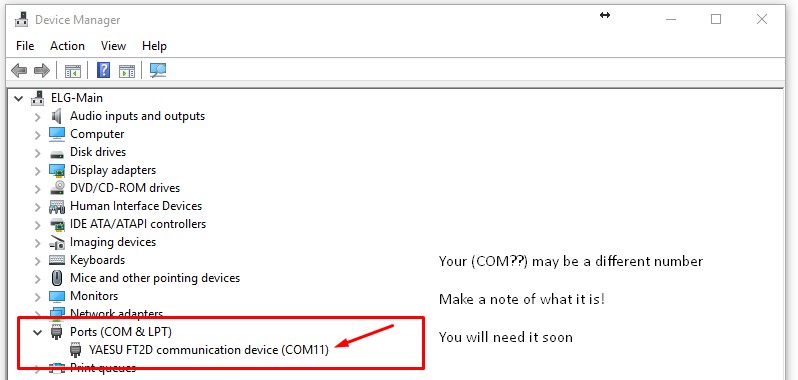
Bron: hamgear.wordpress.com
The AMP-25 series VHF / UHF Amplifiers

The recently announced BTech Digital and Analog amplifier series puts a whole new spin on mobile operation. It performs more like a mobile than it does a power amp. The D series are true TDMA Tier2 DMR amplifiers.
Note: This review was done using an Anytone D868UV on both DMR and analog.
In the Box
Included with the 40W Mobile Amp are:
– Mounting Bracket
– 3′ Interface Control Cable (Kenwood K1 connectors)
– 3′ RF connect cable (SMA-M to SMA-F)
– Microphone and Hanger
– All necessary mounting hardware
– User Guide
General Description
– UHF or VHF Power Amplifier
– 2-6W > 20-40W Output
Modes of operation include:
| V25 U25 |
V25D U25D |
Analog (FM)
C4FM (Fusion)
P25 (Phase 1)
NXDN
IDAS
dPMR
MPT1327 |
> DMR Tier II (TDMA)
> P25 (Phase 2)
Analog (FM)
C4FM (Fusion)
P25 (Phase 1)
NXDN
IDAS
dPMR
MPT1327 |
A Different type of Mobile Amplifier
I found these to be much more than a typical power amplifier. Although they can function as a simple ‘In and Out’ power amp, this is about as close to a full mobile as you can get. Although the driving  force was my DMR handheld sitting in my cup holder, the transmit audio was that of the included hand microphone and the receiver audio out was coming through the built in speaker driven by a four watt audio amplifier.
force was my DMR handheld sitting in my cup holder, the transmit audio was that of the included hand microphone and the receiver audio out was coming through the built in speaker driven by a four watt audio amplifier.
Transmit Power
I tested the power on two different models. The VHF V25 (non TDMA) and the U25D for UHF DMR. The power was tested using the analog side of both into a calibrated Bird Termaline wattmeter. The maximum current drain from my 13.6V 30A power supply was just under 6A. This is low enough for the amp to be powered by the 10A accessory jack in your vehicle.
Enclosure
The basic frame measures 4.6″W x 1.3″H x 5.5″D (excluding the SO-239) and weighs in at 26oz. I was curious to see the internal layout of the amp and to no surprise, there was a 5/8″ finned heat sink spanning the entire length and width of the case along with air vent along the back of the enclosure.
curious to see the internal layout of the amp and to no surprise, there was a 5/8″ finned heat sink spanning the entire length and width of the case along with air vent along the back of the enclosure.
Operating Modes
These are single band amplifiers.
V25(D) = VHF 136-174MHz
U25(D) = UHF 400-480MHz.
Note: The V25D and U25D were designed to include DMR Tier II (TDMA) and P25 Phase 2 along with all other modes. Their operation varies slightly.
V25 / U25
To operate VHF through the UHF (U25) amplifier, or UHF through the VHF (V25) amplifier, simply power off the amplifier. This will allow you to run straight through directly to the antenna without power amplification on that band.
V25D / U25D
These amplifiers will only operate within their specified VHF or UHF range. This is due to the circuit switching design of DMR Tier II and P25 Phase 2.
Hook Up
The simplest configuration is using the included RF cable to attach the radio to the amp. You could add a Spkr/Micr to the handheld, but you would still be bypassing some of the best features.
I use the two included cables. The 3′ RF cable to attach the radio to the amp, and the control cable. This allows me to use the full size hand microphone as well as connecting the four watt audio amp powering the speaker. The power included power cable is compatible with handhelds using the standard two pin Kenwood style connector, such as an MD380, D868, GD77, UV5R, F8HP, UV82, etc.
allows me to use the full size hand microphone as well as connecting the four watt audio amp powering the speaker. The power included power cable is compatible with handhelds using the standard two pin Kenwood style connector, such as an MD380, D868, GD77, UV5R, F8HP, UV82, etc.

I use an Anytone D868 on DMR as well as analog with the hookup diagrammed below. Depending on your radios antenna jack, you may need to pickup an SMA-M to SMA-M adapter.
Convenience
All channel selection and volume adjustments are done using the handheld. No duplicate programming or code plugs are necessary. Whatever is in my handheld is what I operate in the mobile
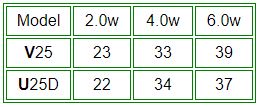
Operating my handheld in the low power position, I still get 22W out on UHF and my handheld’s battery life remains excellent, but high power gives me a solid 39W.
Conclusion
I was glad to see someone finally develop what is a full featured mobile amplifier capable of DMR as well as all other modes including C4FM and D-Star that is small enough to mount in the car, boat, and on top of your computer. This amplifier is Part 90 certified and definitely worth considering.
Available from Amazon: V25 V25D U25 U25D
and 

VHF /UHF
Digital / Analog
Mobile Power Amplifiers